Summary:
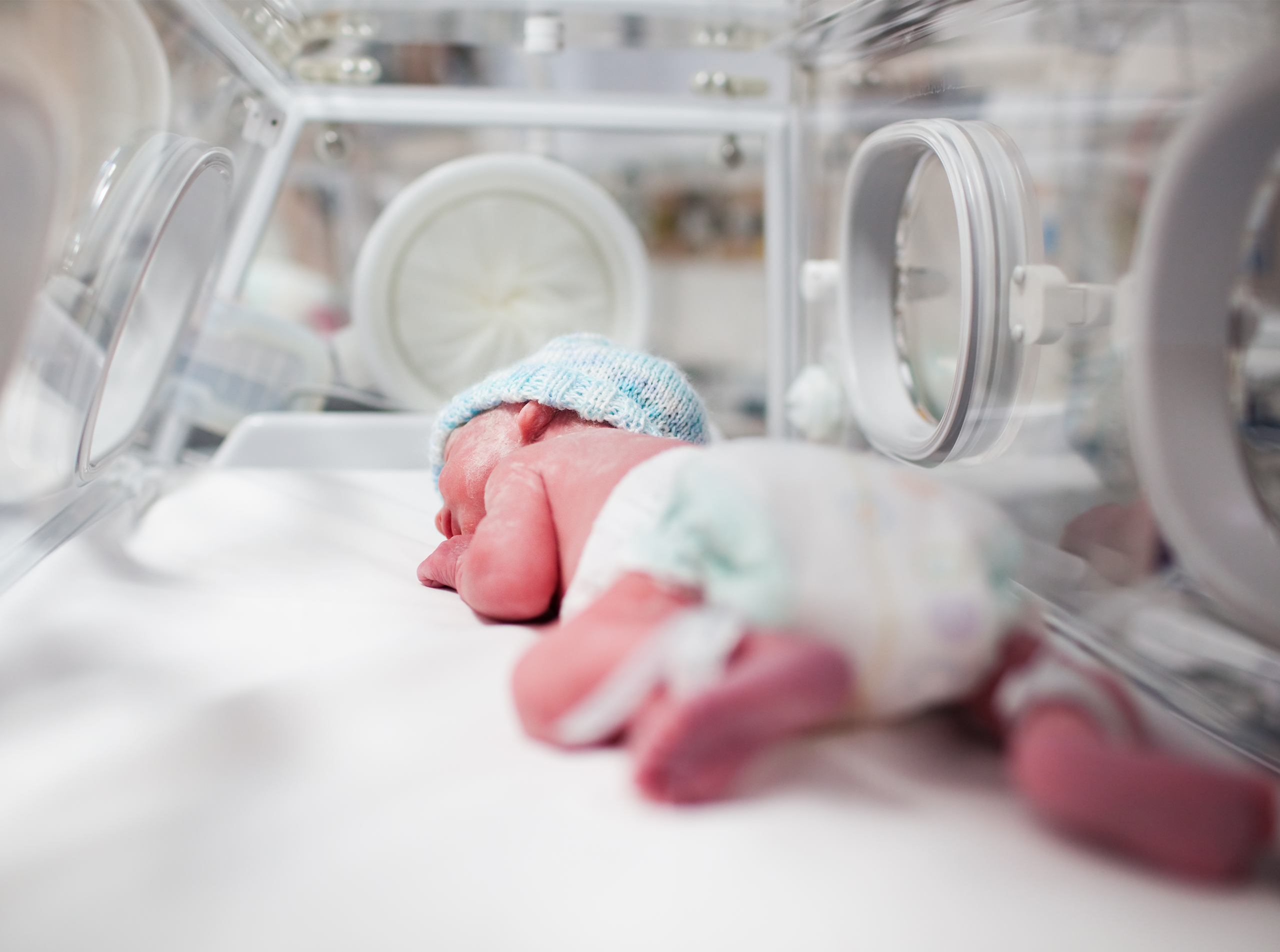
This whitepaper explores how clinicians balance protecting the fragile, developing brains and lungs of premature infants in the NICU. This process is a delicate tightrope walk in which CO2 plays a key role. Because CO2 is a major factor in both cerebral blood flow and delivering mechanical ventilation, monitoring these levels continuously is a vital part of the clinical picture. Transcutaneous CO2 monitoring can enable clinicians to implement care strategies that prioritize both brain and lung protection for these fragile infants.
Preview:
CO2 and the lungs
The very same ventilatory support that can help keep CO2 within safe ranges for brain protection can also damage the lungs without careful consideration. Failing to deliver enough volume can result in derecruitment and atelectasis. Delivering too much risks overdistension and volutrauma.
In this way, the brain and the lungs are in constant tension – what protects one can harm the other. To prioritize lung protection and avoid potentially harmful airway pressures, respiratory teams may employ a strategy of permissive hypercapnia, which can help keep plateau pressures within a safe range, but could put the brain at risk. Prioritizing the brain may require increased ventilator settings that damage the lungs. In these scenarios continuous visibility to CO2 can be a powerful, even vital, tool to balance both priorities.
Transcutaneous CO2 Monitoring (tcPCO2)
Continuous CO2 monitoring can be a valuable tool when care teams employ permissive hypercapnia, as it can allow them to keep a close eye on how the patient is responding and to react quickly to unexpected changes or spikes. It can also be an important component of…
Meet the tCOM+
Developed with care, designed for confidence.
The tCOM+ offers continuous monitoring of tcPCO2, SpO2, and PR with a sleek new look and feel. This latest model includes significant software advances that improve workflow for providers, while continuing to support reduced blood draws and proactive ventilator management across care areas.